Metal spinning process
- Shear Spinning
- Flowing Spinning
- Necking-in
- Edge Flanging
Shear Forming
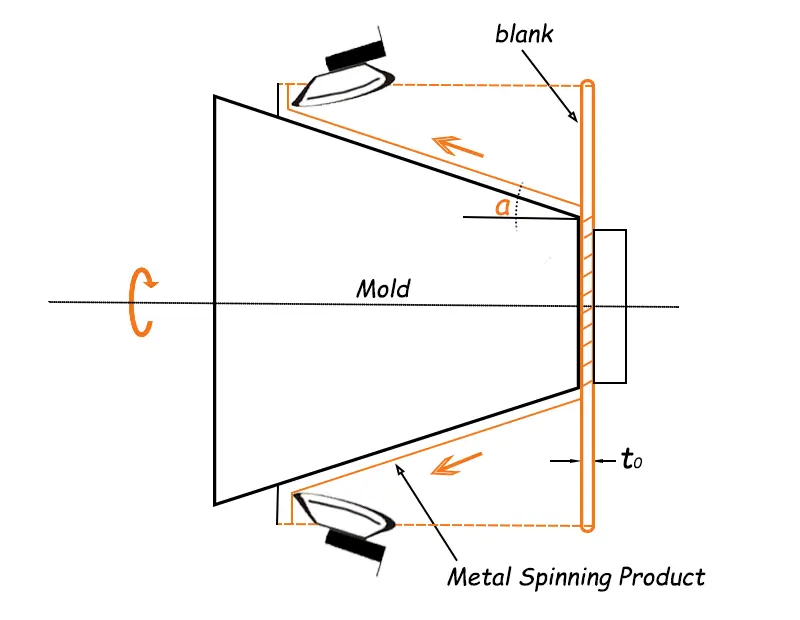
Shear spinning, which refers to the forced spinning of conical components, involves the installation and securing of sheet or conical blanks on a mold. During spinning, the spinning roller rotates together with the workpiece and the mold, deforming the workpiece point by point to achieve the required wall thickness and angle. A conical component can be formed from flat stock in a single spinning operation.
As illustrated, since the outer diameter of the blank remains unchanged, the thinning of the product’s wall thickness is represented as the original thickness t0 = N*sinα, where the wall thickness is reduced. The wall thickness of the finished product is thinner than the thickness of the plate blank. Conical parts with a cone angle α in the 12° to 80° range can be produced in this manner.
This spinning method features short forming times and high forming precision. Additionally, the blank’s initial shape does not have to be circular.